
The integration of XR (Extended Reality) and Metaverse services involves leveraging cutting-edge technologies to create immersive digital experiences. Companies like XR Labs specialise in developing custom Metaverse platforms that offer unique and tailored experiences to users, integrating with various enterprise systems and game engines for cross-platform compatibility. Some firms like Lovelace, Propel MaaS, Touchcast, MVB Worlds, and MetaScapes, provide services like custom XR development, Metaverse integration, XR consulting, and training simulations, catering to diverse industries and pushing the boundaries of XR technology. NTT DATA emphasises the challenges and opportunities in building the XR & Metaverse economy, highlighting the importance of collaboration among different players to enable dynamic solutions and ensure privacy, compliance, and efficient network management within the Metaverse environment. These sources collectively underscore the transformative potential of integrating XR and Metaverse services across industries while addressing key technological, economic, and social considerations for a seamless digital future.

Some examples of XR and Metaverse services include Lovelace, Propel MaaS, Touchcast, MVB Worlds, and MetaScapes. These services are part of the Metaverse as a Service (MaaS) model, which allows companies to create, host, and control virtual environments and experiences within the Metaverse. Lovelace, Propel MaaS, Touchcast, MVB Worlds, and MetaScapes are platforms that enable users to build their digital experiences in the Metaverse without the need to develop entire ecosystems from scratch, making it more accessible for businesses and creators to leverage the opportunities offered by the Metaverse.
Challenges & potential solutions for businesses regarding this integration
The challenges of integrating XR and Metaverse services include economic issues, persistent connectivity problems, technology lagging behind, and challenges rooted in user psychology. Economic challenges involve establishing incentives for users to engage across different platforms, while persistent connectivity issues and the need for decentralised accessibility pose technical hurdles. Additionally, the lag in technology development to integrate various platforms and the user preference for familiar ecosystems present psychological barriers to seamless integration. Overcoming these challenges requires addressing commercial and technical issues, fostering interoperability, and developing cross-platform ecosystems to enhance user experiences and facilitate the transition towards a more interconnected Metaverse environment.
Businesses can overcome the challenges of integrating XR and Metaverse services by focusing on key strategies and solutions. Firstly, addressing interoperability issues is crucial to ensure seamless user experiences across different platforms within the Metaverse, allowing users to move between worlds effortlessly. Implementing strong privacy and security measures to protect user data is essential, considering the sensitive information collected in the Metaverse, such as location and biometric data. Moreover, ensuring accessibility for all users, regardless of physical or financial factors, by making VR/AR/MR headsets and software solutions affordable and easy to use can broaden the reach of Metaverse services. Additionally, navigating the regulatory landscape by developing clear regulations for the Metaverse can create a safe and fair environment for businesses and users alike. By focusing on these aspects, businesses can navigate the challenges and unlock the full potential of integrating XR and Metaverse services to create immersive and engaging digital experiences.
Businesses can ensure the security of XR and VR technologies by implementing robust cybersecurity measures and following best practices. It is essential for businesses to prioritise basic cybersecurity hygiene, such as keeping devices and software up to date with the latest security patches and firmware updates. Utilising VPNs when online, being cautious when installing applications from unknown sources, and carefully handling personal information are crucial steps to enhance security in XR and VR environments. Moreover, businesses should review privacy policies to understand data collection practices, verify the identity of other users, and consider using encryption tools to protect sensitive information and prevent cyber attacks. By focusing on these security measures, businesses can safeguard XR and VR technologies, protect user data, and create a safe and trusted environment for immersive experiences.
Encryption methods in XR and VR technologies: Their differences and security mechanisms
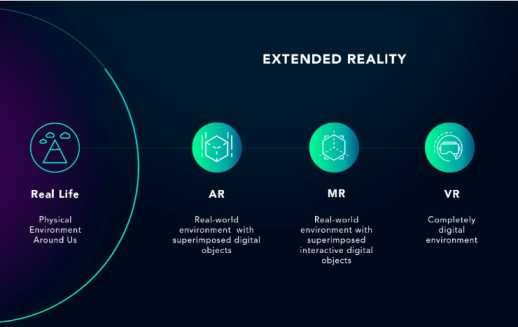
Encryption methods in XR and VR technologies differ based on the specific applications and data involved. In XR technologies, such as AR and MR, encryption focuses on securing extensive data collection about users’ bodies and environments, which can lead to making sensitive inferences about individuals or digital fingerprinting for tracking purposes. On the other hand, VR technologies emphasise encrypting VR data both in transit and at rest to prevent unauthorised access to sensitive information like images, audio, video, biometrics, and location data. While XR encryption addresses the complexities of processing and sharing large volumes of personal data for immersive experiences, VR encryption prioritises protecting data during transmission and storage to safeguard user privacy and prevent cyber threats. These distinctions highlight the tailored encryption approaches required to secure the diverse data types and functionalities inherent in XR and VR technologies.
Some specific encryption algorithms used in XR and VR technologies include AES-256, SSL/TLS, and VPN. These encryption methods play a crucial role in securing sensitive data in transit and at rest within XR and VR environments, protecting information such as images, audio, video, biometrics, and location data from unauthorised access and cyber threats. By implementing strong encryption algorithms like AES-256 and SSL/TLS for secure data transmission, as well as utilising VPNs for remote access, businesses and developers can ensure the confidentiality and integrity of data in XR and VR technologies.
Some encryption methods used to secure XR and VR technologies include transport layer security (TLS) for encrypting data transmitted between devices and cloud servers, ensuring secure communication channels. Additionally, implementing end-to-end encryption for sensitive data exchanged within XR and VR environments can enhance security by encrypting information from the sender to the recipient, preventing unauthorised access. These encryption techniques play a crucial role in safeguarding user data, protecting privacy, and mitigating cybersecurity risks in XR and VR technologies.
Current Statistics and Numbers: A Tale of the Evolution
- The global metaverse market is expected to reach $936.57 billion by 2030.
- The virtual fitting room market is predicted to reach $13 billion by 2028.
- The global AR, VR, and MR market is expected to roughly reach $250 billion by 2028.
- The XR market is projected to hit $333.16 billion by 2025, up from $42.55 billion in 2020.
- The VR and AR market will also keep growing, reaching sales of 71 million devices in 2025—up from 11 million in 2021.
- Enterprise adoption of AR is expected to increase 66% per year through 2026.
- The metaverse market is presently estimated at $38.5 billion.
- North America is predicted to dominate revenue share until 2032, while Asia Pacific is projected to have the highest CAGR.
- Several prominent tech companies like Microsoft, Autodesk, Nike, Block, and Shopify see the metaverse as an unprecedented opportunity to expand their reach.
- Metaverse AR & VR hardware is estimated to earn US$1.17 billion in 2023, with a projected growth of 15.36% yearly to $3.19 billion by 2030.
- Global AR and VR shipments headsets are predicted to reach 32.76 million in 2024, and an estimated 43.87 million by 2025.
- The European AR/VR market will grow from $2.8 billion in 2021 to $20.9 billion in 2025.
The integration of XR (Extended Reality) and Metaverse services has evolved significantly over the years, with advancements in technology and increasing adoption across various industries. The Metaverse, a networked space where human and automated entities interact, has gained momentum due to technological advancements and the COVID-19 pandemic, leading to substantial investments and predictions of its impact on the future of the internet.
XR technologies, including AR (Augmented Reality), VR (Virtual Reality), and MR (Mixed Reality), have been transforming daily life and the service industry. For instance, in education, XR offers immersive learning environments and practical training simulations, while in healthcare, it revolutionises patient care through telemedicine and medical training simulations. These technologies are expected to dominate by 2040, offering greater utility to the public and holding promise for various industries, including education, healthcare, manufacturing, retail, workforce training, and virtual patient monitoring.
The Metaverse’s development has also been influenced by the rise of Web3 services and technologies, such as blockchain and decentralised concepts, which make it more secure and private. As the Metaverse expands, it is becoming more accessible to everyone, with opportunities for digital artists and content creators to monetise their work on Metaverse service platforms.
Despite the optimism surrounding the Metaverse’s future, there are challenges and scepticism about its widespread adoption. Some experts wonder if fully-immersive VR experiences will gain widespread popularity, as virtual spaces may not fully satisfy interpersonal dynamics and can be expensive, uncomfortable, and disorienting. However, with careful development and responsible implementation, XR and the Metaverse have the potential to revolutionise education, healthcare, entertainment, and various aspects of society.
The integration of XR and Metaverse services has evolved significantly, with advancements in technology and increasing adoption across various industries. While there are challenges to overcome, the potential benefits of these technologies are substantial, and with careful development and responsible implementation, they have the potential to transform daily life and the service industry.
A further look at this integration in Gaming Industry
The integration of XR (Extended Reality) and Metaverse services in the gaming industry has revolutionised the gaming experience, offering immersive and interactive gameplay. Companies like Decentraland, The Sandbox, Epic Games, Meta Platforms (formerly Facebook), and Improbable are at the forefront of this transformation.
- Decentraland: Known for creating a metaverse platform with virtual spaces for multiplayer gaming, Decentraland utilises an Ethereum-backed native token (LAND) and real estate allocation. It has also invested in Decentral Games to enhance its gameplay hosting capabilities.
- The Sandbox: This platform allows users to play, create, own, and govern virtual spaces. It operates on user-generated crypto and NFT assets, collaborating with global brands to deliver unique experiences. Notable collaborations include Standard Chartered and Snoop Dogg for expansive metaverse worlds.
- Epic Games: Renowned for Fortnite, a world-building platform for popular games, Epic Games has enabled major brands and artists to host concerts using its technologies. It offers tools for developing characters, animations, and realistic XR avatars like MetaHuman.
- Meta Platforms: Formerly Facebook, Meta Platforms leads the XR market with its Quest headset lineup and immersive Horizon Worlds platform for game creation and publication. Meta is synonymous with virtual reality gaming and is making significant advancements in metaverse technologies.
- Improbable: This emerging metaverse infrastructure company aims to facilitate vast multiplayer worlds with innovative technologies. Improbable is focused on increasing concurrent users and exploring new possibilities within the metaverse space.
These examples showcase how XR and Metaverse services are reshaping the gaming industry by offering new dimensions of interactivity, creativity, and social engagement to gamers worldwide.
Conclusion: A Bright Future
In conclusion, the integration of XR (Extended Reality) and Metaverse services represents a transformative shift in how we interact, communicate, and engage with digital environments. As we delve deeper into the era of the Metaverse, the opportunities and challenges presented by these technologies are becoming increasingly apparent. The evolving economy, expanding ecosystem of creators and users, and the growing adoption of XR technologies are paving the way for a future where virtual and physical worlds seamlessly intertwine.
Looking ahead, the futuristic aspect of this integration holds immense promise. With advancements in XR devices, immersive experiences will become more dynamic, realistic, and user-friendly. The Metaverse is poised to unlock new dimensions of social interaction, entertainment, education, and commerce. As technology progresses, XR projects will become more sophisticated and useful across various industries like gaming, healthcare, retail, and real estate.
Ultimately, the fusion of XR and the Metaverse is propelling us towards a future where boundaries between reality and virtuality blur, offering unparalleled immersive experiences that have the potential to reshape how we live, work, and play in the digital age.
